Nuclear in Bullet Points
Written by on May 29, 2025
The goal of this page is to provide a quick summary of key facts related to Nuclear Energy. Deeper Analysis and Explanations are left to dedicated articles and sources. I care a lot about acknowledging the work of other people, so here is a list of websites, associations and institutions from which these data are mostly based.
As always if you think that some of the data are not correct or are presented in a biased way, please let me know ( in a polite way please).
Before reading further test your knowledge about nuclear by taking our quiz here .
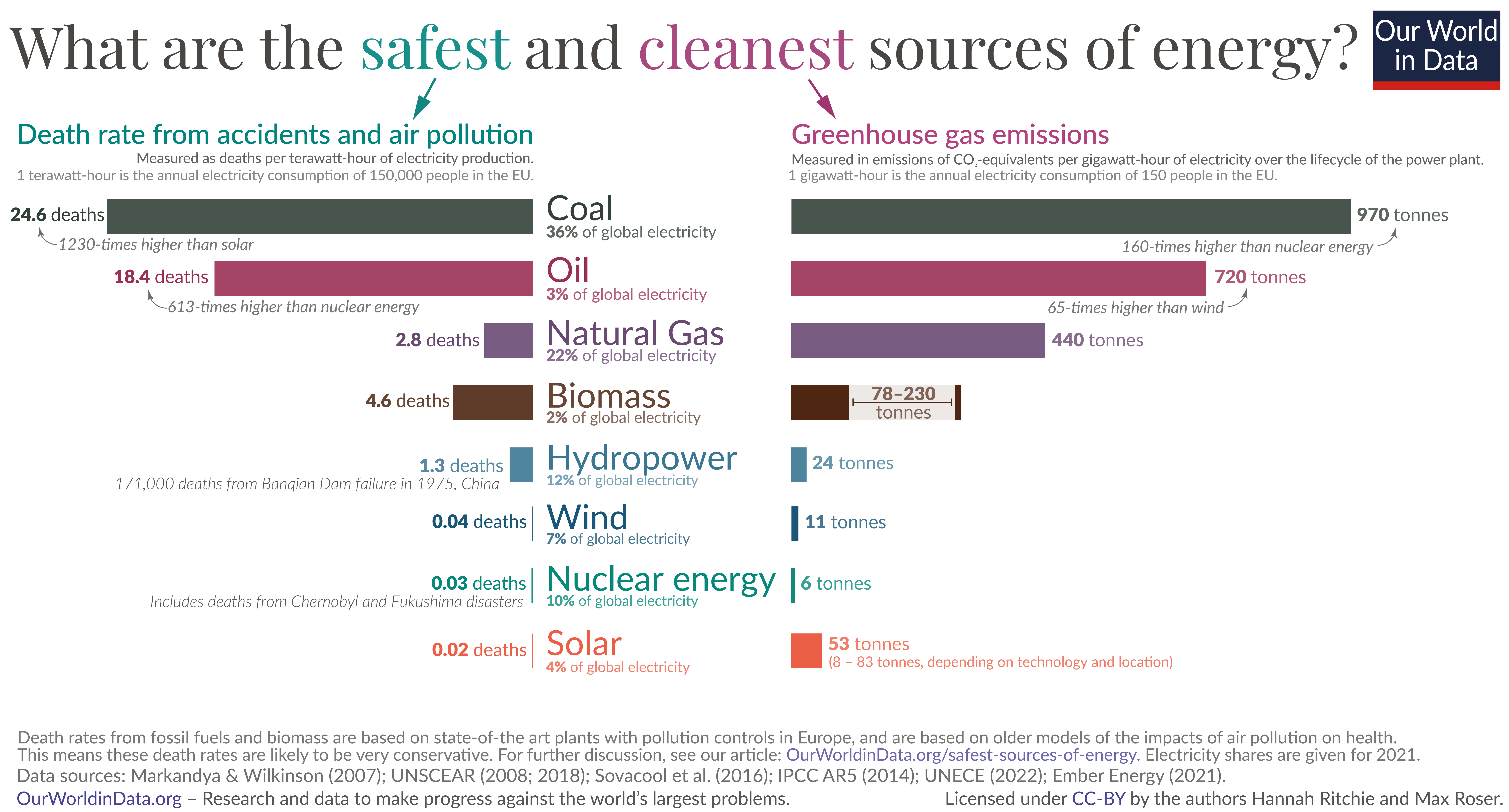
Nuclear Safety
- Chernobyl: between 300 and 500. Numbers from OurWorldInData
- 2 workers died in the blast
28 workers and firemen died in the weeks after due to acute radiation Syndrome (ARS)
19 ARS survivors had died later by 2006; most were from causes not related to radiation, but it’s not possible to rule all of them out (especially five that were cancer-related)
- 96-385 due to thyroid cancer due to Milk contamination.
Fukushima: 1 dead because of actual radiation, 2314 because of evacuation
Nuclear Carbon Emissions
Nuclear Construstion Items
Olkiluoto-3 in Finland: based on the European Pressurized Reactor (EPR) model
Original cost was €3 billion, actual final cost is around €11 billion.
Started in 2005, original completion timeline should have been in May 2009 but it entered service only in Aprile 2023.
More info about Nuclear Energy in Finland can be found
hereFlamanville 3 in France: based on the European Pressurized Reactor (EPR) model
Original cost was supposed to be €3.3 billion, latest cost estimations are €19.1 billions.
Started in 2007, original completion timeline should have been in 2012 but it was connected to the grid in December 2024.
Korea Ulchin Unit 5 in South Korea. Started in October 1999 and finished in July 2004 for a total of around 5 years
Onagawa Unit 3 in Japan. Started in January 1998 and finished in January 2002 for a total of around 4 years
Yangjiang Unit 1 in China. Started in December 2008 and finished in March 2014 for a total of around 5 years
Specialised Workforce: building nuclear power plants requires a specifically trained workforce. Countries that build nuclear plants often can benefit from economy of scale.
Regulations: some countries might have regulations that make it easier to build fast.
Engineering Complexity: building multiple times the same type of nuclear power plant likely helps reducing the times.
Nuclear Costs
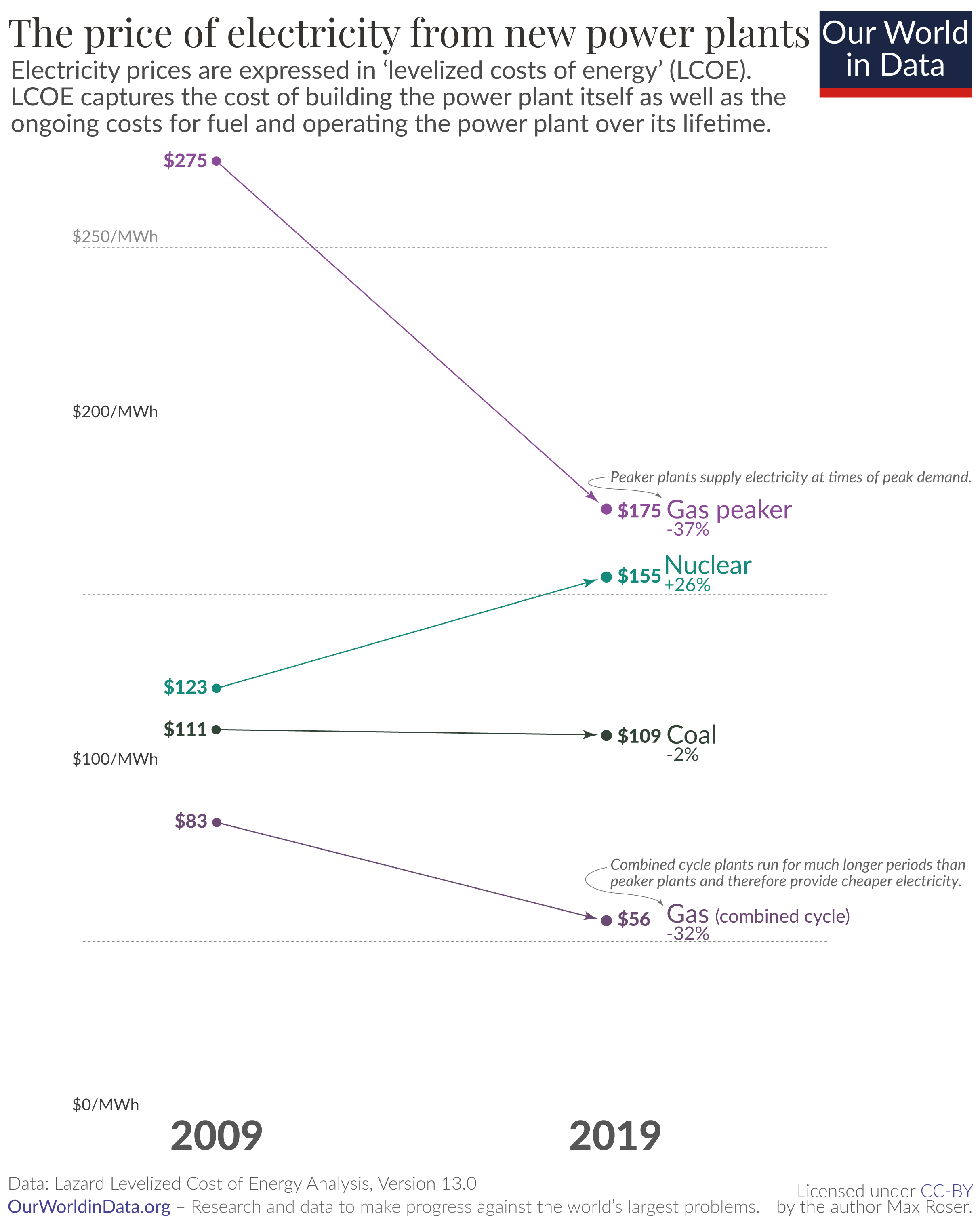
It’s quite hard to compare different electricity sources because for example renewables require energy accumulation and investment in the grid which are typically not included in their costs.
Nuclear Waste
90 % of the waste is considered Low-Level and is mostly made of normal objects that became lightly radioactive after being used in the nuclear power plant. Example of this are work clothes. The radioactivity in these objects is short lived.
7 % are intermediate level waste, like filters and steel components.
3% constitutes high level waste. Note that about 97% of the fuel can be recycled.
Nuclear Capacity Factor
Unfortunately most of the other climate friendly electricity source have a low capacity factor ( with the exception of hydropower)
Nuclear Power Plants Duration
- Typically Nuclear power plants lasts for 40 to 60 years.
- Some countries are considering to extend this duration to 80 years.
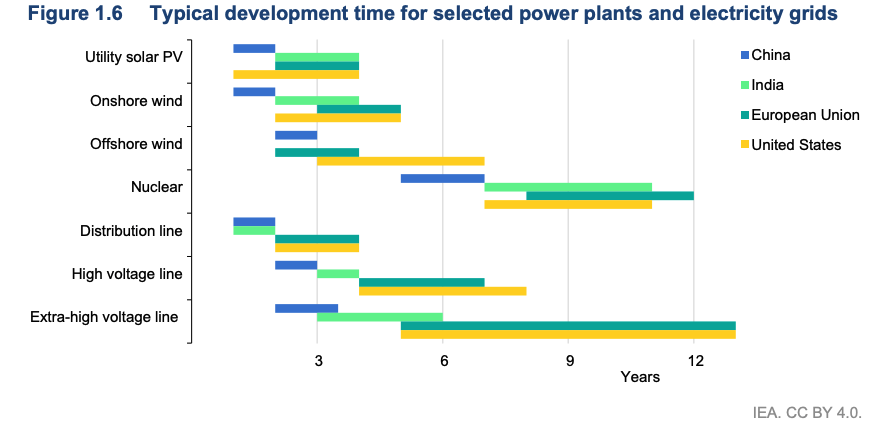
Nuclear Power Plants Development
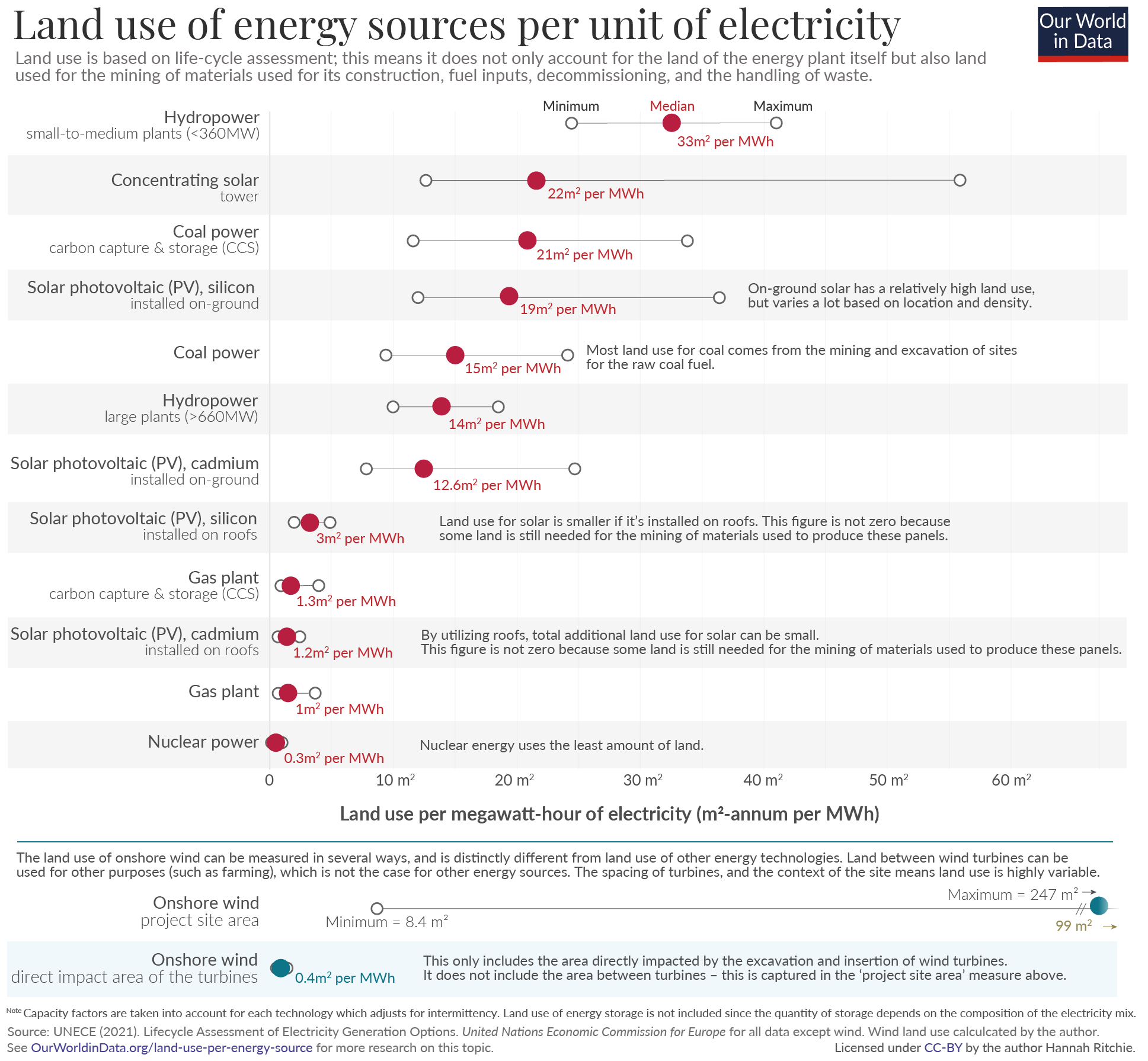
Nuclear Land Use
Sources
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.